The Complete Guide to Mobile App Development

Are you thinking about developing a mobile app for your business? You’re not the only one.
Your competitors are probably thinking about it, too. They may even be working on—or already have—an app for their business.
Much like websites, social media, and other marketing and branding tools, mobile apps offer a highly effective way to build stronger customer relationships.
Here are just a few benefits you can gain from developing an app for your business:
1. Increased Brand Awareness
How many times do you look at your phone in a day? When customers put your app on their phones, they’ll be reminded about your brand every time they look at the screen. And if your app engages them with notifications, that awareness skyrockets.
And that’s not the only way apps increase your brand’s visibility. Your presence in app stores means everyone searching for apps in your category will also see your brand. Your business is therefore seen as tech-savvy and perhaps even forward-thinking.
2. Higher Customer Engagement
Your customers don’t want to talk to you over the phone. They may email you, but they really want you to make doing business as easy as a few taps on their screen.
If your app makes it easy for your customers to buy from you, pay their bills, process a return, use coupons, pre-order new products, and so on? You’ll not only see higher engagement, but you’ll get rave reviews in the app store—boosting brand awareness even more.
Push notifications are another way your app can increase customer engagement. Have you got a special offer or a sale going on? You can push a short message out through your app and have it pop up on your customers’ screens.
3. Improved Customer Service
If customers don’t want to talk to you to place an order, they certainly don’t want to have to call with a complaint or service need. The easier you make it for them to get help, the more they’ll love you for it.
According to Hubspot, 50% of customers buy more from a brand after a positive customer service experience, and 67% would pay more to get better customer service.
With the right mobile app development, your app can give customers the kind of service they’ll rave about. Some common customer service features include in-app messaging, call and call-back buttons, directions to your nearest store, and the ability to leave feedback.
4. Deeper Customer Insights
Remember how impressed you were when you saw how much you could learn about your customers from website analytics? Mobile apps give you even deeper insights into the behavior of your customers.
You can discover the questions they want answered, the stores they visit most, the app features they find most valuable, and more. This data, in turn, can help you improve the app, develop more effective ads and outreach programs, and deliver the products and features your customers crave.
Mobile Is Here to Stay
More and more, people avoid brick-and-mortar stores and shop online. According to Statista, 22% of retail sales will happen online in 2023, and mobile eCommerce is a significant driver. Nearly half of eCommerce (49.2%) happened via mobile devices in 2020.
As mobile apps take off, businesses like yours will continue developing and improving sophisticated ways to gain buyers’ attention, give them a delightful user experience, learn more about them, and use that information to make sales after-sales.
Types of Mobile Apps
If you go by Google or Apple’s app store categories, there are dozens of types of mobile apps. All of these categories can be divided into six general buckets.
1. Games and Entertainment
This is by far the most popular type of app. It’s also the largest and most competitive category; as of June 2021, games accounted for over a fifth of all apps available in the Apple app store, according to Statista.
2. Social Media
Social media apps are the most used apps on everyone’s phones. Facebook, TikTok, and Instagram lead social apps, while others spike in popularity and fade away.
3. Lifestyle
Lifestyle apps are about fitness, dieting, drinking, dating, music, travel, and other ways of enjoying life. Most include some kind of social media sharing. Examples include MyFitnessPal, OnTap, and Spotify.
4. Utilities
Utility apps are often used, but not flashy or fun. Most of them come with your phone. Some examples are your calculator, calendar, flashlight, reminders, and notes apps.
5. Business and Productivity
Believe it or not, business apps are also enormously popular, and the category is almost as competitive as games. That’s because these are the apps you use to get tedious tasks done quickly. Examples include banking, shopping, and task list apps.
6. News and Information
Every news channel has its own app—including local news outlets. This category also includes apps like WeatherBug, Feedly, Reddit, and LinkedIn (although those last two could also be considered social media apps).
LEARN MORE: Types of Mobile App Development: Native vs. Hybrid vs. Web Apps
The Mobile App Development Process: From Concept to Launch
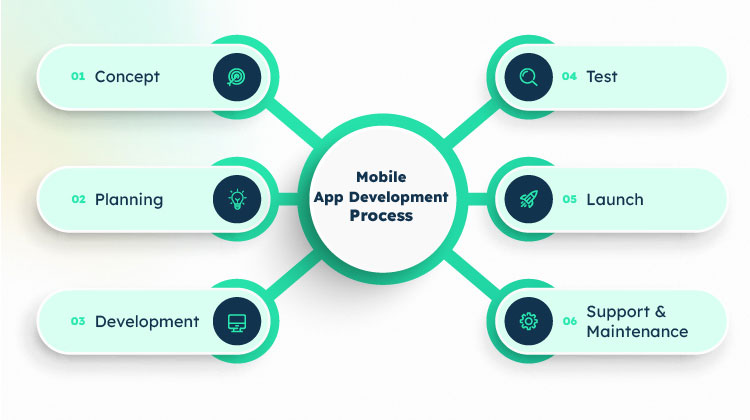
The mobile app development process involves different steps that help turn an idea into an actual app you can use on your phone or tablet.
The first step is called the concept phase. This is when someone comes up with an idea for a new app and thinks about what it will do and who will use it. They might also think about what the app should look like and how it will be helpful. What problem will it solve for the user?
Once the concept is clear, the next phase is planning. The app developers make a plan for how the app will work. They think about the app’s features and how people will use them. They might also make a sketch or mockup to show the app’s appearance.
After planning, it’s time to start building the app—i.e., the development phase. Software developers write the code that makes the app work. They use mobile app frameworks and languages to create the app’s features and functions. This part can take a lot of time and effort because the developers want to ensure the app works well and has no bugs or problems.
Once the app is built, it’s tested. The developers try out the app to make sure it works right and maybe release it to a small group of users to test in the real world. Any issues or errors found in testing are sent back to the developers.
When the app is tested and working well, it’s ready to be launched. Launching means releasing the app to the public so people can download and use it.
After the app launches, the developers might continue to work on it in the support and maintenance phase. They might update the app to add new features or fix any problems. This phase ensures the app stays up to date and keeps working well for its users.
So, the mobile app development process goes from the concept to planning, then development, testing, launching, and finally, maintaining and updating the app. It takes a lot of work, but having a cool and useful app that wows your customers is worth it.
LEARN MORE: The Mobile App Development Process: From Concept To Launch
How Long Does It Take to Build a Mobile App?
Like cost, the time it takes to develop a mobile app depends on its complexity—the more complex, the longer the development time. Generally speaking, it takes three to nine months to create Version 1.0 of your app.
If this seems like a lot, remember that not all this time is spent on actual coding. The steps in mobile app development often include:
- Creating project brief (1-2 weeks)
- Researching app with developers (4-5 weeks)
- Designing the app (6-12 weeks)
- Developing and prototyping (6-12 weeks)
- Releasing app (1-2 weeks)
An experienced mobile app developer should be able to give you an accurate estimate once they’ve scoped the project. Beware of companies that overpromise, however. If a developer tells you they can build your highly complex app in a month, for example, they’ll most likely underdeliver.
Understanding the User Interface and User Experience Design in Mobile App Development
User Interface (UI) and User Experience (UX) design are essential to creating an easy and enjoyable mobile app.
User Interface design is all about how the app looks and how people interact with it. UI designers choose colors, shapes, and fonts that make the app look friendly and inviting. They also decide where to place buttons and menus so they are easy to find and use. The goal is to make the app look appealing and easy for people to understand how to use it.
User Experience design is about how people feel when they use the app. UX designers think about how people will use the app and what they want to do with it. They want to make sure the app is easy to navigate and that people can find what they’re looking for without getting confused. They also want to ensure the app works smoothly and has no problems that might frustrate users.
App developers work closely with UI and UX designers to make sure the app looks great and is easy to use. They collaborate to create a design that will make people happy and want to keep using the app.
Essential Features to Include in Your Mobile App
When creating a mobile app, several essential features can make it more valuable and enjoyable for users. Here are some of those crucial features:
User Registration and Login
This feature allows users to create accounts and log in to the app. It helps personalize the user experience and enables features like saving preferences, accessing personalized content, and keeping track of user data.
Intuitive User Interface
A user-friendly interface is crucial for a mobile app. It should be easy to navigate, with clear menus, buttons, and icons. The design should be visually appealing and consistent throughout the app.
Security Measures
Security features are essential for protecting user data and maintaining user trust. Implementing encryption, secure login processes, and data privacy settings can enhance the app’s security.
Push Notifications
Push notifications are messages that pop up on a user’s device to provide important information or updates from the app. You can use push notifications to deliver reminders, alerts about new content or features, or personalized messages.
Search Functionality
A search feature lets users quickly find specific information or content within the app. It is especially useful for apps that have a lot of data or offer a variety of services.
In-App Messaging or Chat
This feature enables users to communicate with each other or with customer support directly within the app. It can benefit social apps, e-commerce platforms, or apps requiring user interaction.
Social Media Integration
Integrating social media allows users to share app content, invite friends, or sign in using their social media accounts. Depending on your mobile app’s purpose, social media integration may help to expand the app’s reach and enhance user engagement.
Offline Functionality
While an internet connection is usually required for most app features, offline functionality allows users to access certain content or perform basic tasks without an internet connection. This can enhance the app’s usability and convenience.
Feedback and Rating System
A feedback or rating system allows users to share their opinions and experiences, providing valuable insights for app improvement. It also helps other users make informed decisions about the app.
App Analytics
Integrating analytics allows developers to collect data about how users interact with the app. It provides valuable insights into user behavior and preferences and helps identify areas for improvement.
These are just some essential features to consider when developing a mobile app. The specific features will depend on the nature of the app, its purpose, and the target audience.
LEARN MORE: Essential Features to Include in Your Mobile App
The Importance of Accessibility in Mobile App Development
Accessibility in mobile app development refers to designing and developing usable and inclusive apps for individuals with disabilities. It involves considering the diverse needs of users and providing features and functionalities that enable equal access and participation.
Accessibility is often legally required, but even when it’s not, it is a crucial consideration for enhancing the user experience for all users. Some aspects to consider include:
1. Inclusivity and Equal Opportunity: Accessibility ensures that individuals with disabilities have equal opportunities to access and benefit from mobile applications. It promotes inclusivity by removing barriers and providing an equitable user experience for all users, regardless of their abilities.
2. Legal and Regulatory Compliance: Many countries have laws and regulations that mandate accessibility standards for mobile apps, especially those used in the public sector or by organizations serving the public. Complying with these accessibility requirements is essential to avoid legal consequences and ensure equal access for all users.
3. Expanded User Base: By incorporating accessibility features, your mobile app can benefit a broader range of users. This includes individuals with visual impairments, hearing impairments, motor disabilities, cognitive impairments, and other disabilities. Making your app accessible opens up opportunities to tap into new user segments and expand the user base.
4. Enhanced User Experience: Accessibility considerations often lead to improvements in the overall user experience for all users. Designing for accessibility encourages clear and intuitive interfaces, consistent navigation, and well-organized content, benefiting users with or without disabilities. A better user experience can result in increased user satisfaction and engagement.
5. Improved Usability and Efficiency: Accessibility features, such as alternative input methods and text-to-speech capabilities, can enhance the usability of mobile apps for all users. These features can streamline interactions and improve efficiency, benefiting individuals with disabilities as well as users in diverse environments or contexts.
6. Corporate Social Responsibility: Incorporating accessibility in mobile app development demonstrates a commitment to social responsibility. It highlights your company’s dedication to diversity, inclusivity, and equal opportunities, which can positively impact your reputation and relationships with customers, employees, and the broader community.
7. Future-Proofing and Scalability: By considering accessibility during the development process, mobile apps are more likely to be adaptable and scalable. They can accommodate future updates, changes in technology, and emerging accessibility standards without requiring significant modifications or redevelopment.
8. Ethical Considerations: Accessibility is an ethical imperative in mobile app development. It recognizes the inherent dignity and rights of individuals with disabilities and ensures they are not excluded or marginalized in the digital world. Prioritizing accessibility aligns with principles of fairness, respect, and social equity.
By prioritizing accessibility in mobile app development, organizations can create more inclusive, user-friendly, and socially responsible apps. It empowers individuals with disabilities to fully participate in the digital community and contributes to a more equitable and inclusive society as a whole.
LEARN MORE: The Importance Of Accessibility In Mobile App Development
Choosing the Right Mobile App Development Platform for Your Business
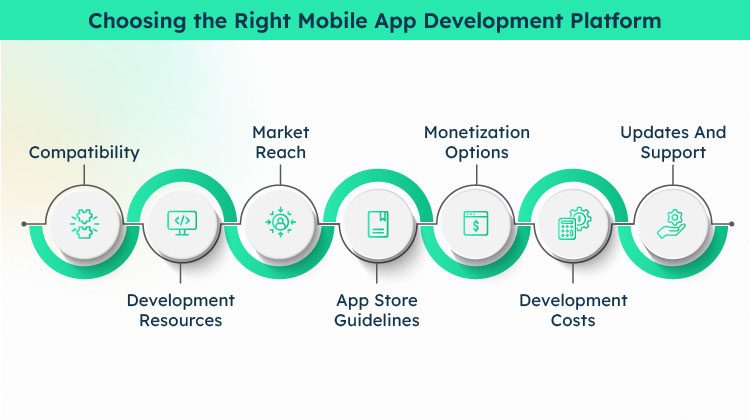
Choosing the right app development platform is crucial when creating a mobile app for your business. A development platform is a foundation that helps build and run your app on smartphones and tablets. Let’s look at some things to consider when selecting a mobile app development platform.
Compatibility
You need to think about the devices your customers use. If most of them have iPhones, you should consider iOS as your platform. If they use Android devices, then Android would be a better choice. It’s essential to pick a platform that is compatible with your target audience’s devices.
Development Resources
Consider the resources you have available. Different platforms require different programming languages and development tools. If you have a team of developers experienced in a particular language, choosing a platform that supports that language might be easier. Having the necessary skills and tools to develop and maintain your app on the chosen platform is important.
Market Reach
Think about the size of the user base for each platform. Android has a larger market share globally, while iOS tends to have more users in certain regions like the United States. Consider your target market and choose a platform that gives you access to a larger number of potential users.
App Store Guidelines
Each platform has its own set of guidelines and rules that apps must follow to be accepted on their respective app stores. It’s essential to review and understand these guidelines before choosing a platform. Some platforms may have stricter guidelines or more complex approval processes.
Monetization Options
If you plan to generate revenue from your app, consider the monetization options available on each platform. Android and iOS offer various ways to monetize your app, such as in-app purchases or advertising. Research the options and choose a platform that aligns with your monetization strategy.
Development Costs
Consider the costs of developing and maintaining your app on a specific platform. Some platforms may require additional fees for developer accounts, app store submissions, or updates. Evaluate your budget and choose a platform that fits within your financial constraints.
Updates and Support
Check the platform’s track record for updates and support. Platforms that regularly release updates and provide good support can help ensure your app remains compatible with new devices and operating system versions. This can also contribute to a better user experience and overall satisfaction.
Android Pros and Cons
Manufacturers like Samsung, Acer, Dell, HTC, Lenovo, Sony, LG, and more use the Android open-source environment for running apps on hardware such as smartphones, tablets, and wearables. Let’s look at the pros and cons of the Android platform.
Pros of Android
Huge international smartphone base. Globally speaking, Android has the largest smartphone user base by far. According to StatCounter, Android owned 73% of the worldwide mobile operating system market share in 2020, while iOS held 27%. (However, the picture drastically changes when you break it down by region. More on that in a minute.)
More features. Because Android is an open-source system, Android developers receive access to many features unavailable or restricted in iOS applications, an advantage particularly useful to custom Android app development companies.
Quick and inexpensive app release. Android apps can be quickly published to the Google Play app store, sometimes in just a few hours. In Android app development, publishing an app costs only $25.
Cons of Android
Fragmentation. Android devices from various manufacturers come with so many screen sizes, resolutions, and other hardware differentiators that development teams might need to spend more time customizing features to work with specific devices.
Testing can be lengthy. Manufacturers vary, too, in terms of when they adopt different versions of the Android OS. In conjunction with hardware variations, this can add time to QA testing for Android app development companies.
Development costs can be high. If development and testing are lengthy procedures, this can raise your overall costs substantially.
iOS Pros and Cons
In contrast to Android, Apple’s iOS is a closed system. iOS developers can only create apps for Apple hardware devices—iPhones, iPads, Apple Watches, and so on.
Pros of iOS
High-end demographics. While Android enjoys the lion’s share of the global market, iPhones are more prevalent in wealthier countries. Statista reports that 58% prefer iOS in the US, and 69% prefer Apple over Android in Japan. And Apple users spend more, accounting for 64% of worldwide consumer spending on app stores.
Quicker development time. Because iOS powers only Apple products, iOS developers only need to fit an app to a limited number of devices and screens.
Large installed iPad base. If you’re planning an app that runs on tablets, iOS can be a particularly attractive environment. In the fourth quarter of 2020, Apple continued its perennial lead in the worldwide tablet market, shipping 19.2 million units and capturing 36% of the market share, according to Canalys.
Cons of iOS
Longer release time. Apple’s App Store has strict review guidelines for apps and updates compared to the Google Play Store. Apple might reject an app or update based on its content, security issues, or poor performance. After submitting an app for review, Apple developers can wait as long as a week for an answer.
Lack of flexibility. iOS apps can also be challenging to customize due to the many restrictions of the platform.
Hybrid Mobile Development
Cross-platform mobile development environments allow you to create an app that works on both Android and iOS devices. While this may seem like the way to go, hybrid development does have its drawbacks—namely, an inability to take advantage of the complete feature set of either platform.
By considering the benefits and drawbacks of each platform, you can make an informed decision when choosing the right mobile app development platform for your business. The most important thing to remember is alignment with your target audience, available resources, market reach, and business goals.
Best Programming Languages for Mobile App Development
Your platform choice will help determine what mobile development language to use. Let’s look at some of the most popular languages for each platform.
Android Development: Java vs. Kotlin
First introduced by Sun Microsystems back in 1995, Java is an object-oriented, open-source environment used widely in development for Android and other operating systems. Java app development is easy, with code that looks much like C/C++. Java Android apps have access to extensive libraries for everything from logging to unit testing, for example. The Android Studio integrated development environment (IDE) contains built-in Java source files.
On the other hand, some Android mobile app development companies find Java’s repetitive syntax problematic.
Unveiled by Google in 2017, Kotlin for Android requires developers to write less code than Java, accelerating development. Kotlin also eliminates some Java-specific issues, such as NullPointerException. And it offers access to all frameworks and libraries written in Java.
However, the learning curve for Kotlin is rather steep, and Kotlin hasn’t yet built up nearly as much community support as Java.
iOS Development: Objective C vs. Swift
When Apple’s App Store opened in 2008, every app was written in Objective C. One important reason for Objective C programming is that Apple Objective C is a relatively user-friendly language for those new to object-oriented development. Apple also viewed the development environment as robust and scalable. Additionally, as a C language superset, Objective C has many functions that deal specifically with graphics, I/O, and display functions.
In 2014, Apple introduced Swift iOS development as an even easier and faster method for iOS development. Swift app development includes a “Playgrounds” feature for helping iOS developers teach themselves to move from Objective C to Swift programming. Now gaining widespread adoption by iOS developers, Swift development can be used separately or in conjunction with Objective C.
Ionic App Development
The Ionic development environment lets you create hybrid iOS, Android, and web apps using HTML and CSS. Ionic provides a library of mobile-optimized UI components, gestures, and tools. Apps are rendered using Web Views, a full-screen and full-powered web browser. Ionic can produce elegant mobile UIs, but rendering times can be slow on larger apps.
Hybrid apps built with Ionic cannot access native features like the camera, contacts, and GPS right out of the box. Instead, Ionic developers use Cordova plug-ins to integrate native features into the app. Ionic can be used independently with plain vanilla JavaScript or with a React, Vue, or Angular framework.
React Native App Development
React Native is a JavaScript environment for cross-platform mobile development based on ReactJS. Developers working in React Native use code compiled from a single JavaScript codebase. React Native allows the reuse of both UI components and the logic layer between Android and iOS.
Like ReactJS, React Native replaces HTML and CSS for UI development with JSX, an XML markup language that compiles UI components into native platform-specific components. For example, a React Native text component will render natively on Android as a TextView, but on iOS as a UILabel.
Vue Native
Vue Native is a hybrid development environment introduced in 2018. The goal of Vue Native is to build lightweight but richly featured cross-platform mobile apps. Essentially a wrapper around React Native APIs, Vue Native is designed to let developers take the best features from both React Native and VueJS.
One difference between React and VueJS is that VueJS developers can work in JavaScript, HTML, or other languages. Vue divides components into presentational and logical categories. Vue recommends that Vue developers use templates for presentational components and rendering/JSX for logical components.
Angular Native
A major rival to React, Angular is a front-end framework. Unlike React, Angular does not require integrations with external libraries and tools to allow developers to start building an app. Developers can use either JavaScript or the easier TypeScript superset for coding in Angular.
NativeScript
For its part, React Native is seen as competing not with Angular but with NativeScript, an offering from development firm Telerik. Although it can also be used independently or with Vue, NativeScript is fully supported by Google to share most of its code base with web apps in Angular development. NativeScript is available with a full stack of tools, services, and solutions for both Android and iOS, including code encryption and security.
Flutter Native App Development
Flutter is a new and increasingly popular widget-based UI toolkit from Google for building graphically “beautiful” Android, iOS, web, and desktop apps from a single code base. App developers working in Flutter use Google’s Dart programming language. Flutter also contains a hot reload feature meant to let Flutter mobile developers build UIs, experiment with new features, and fix bugs with sub-second reload times without losing state on hardware, emulators, and simulators.
Flutter’s fully customizable widgets include a “Cupertino-style” series for iOS app development. Google eyes expanding app development in Flutter from iOS and Android to Microsoft Windows and Apple’s macOS environments soon.
Xamarin Native
Owned and produced by Microsoft since 2016, Xamarin was originally built by the developers behind the Mono open-source project. Xamarin uses C# and native libraries wrapped in Microsoft’s .Net layer for cross-platform app development across iOS and Android, with support for both Apple Watch and Android Wear. Code for business logic, database access, and network communications can be shared across all platforms, but Xamarin also lets developers create a platform-specific UI code layer.
Most Xamarin developers use Windows computers with Microsoft Visual Studio and Xamarin installed. Developers can generally keep the native look and feel of iOS and Android apps from within Xamarin. Yet, they can also call existing platform code, such as Swift, to achieve platform-specific functions like barcode scanning or PayPal.
LEARN MORE: Best Programming Languages For Mobile App Development
Tips for Successful Mobile App Development Projects
Developing a successful mobile app requires careful planning and execution. Here are ten tips to help you achieve success in your mobile app development projects:
1. Define Clear Goals: Clearly define the goals and objectives of your app project from the beginning. Understand what problem your app is solving or what value it provides to users.
2. Put the Users First: Put your users at the center of your development process. Understand their needs, preferences, and pain points. Design and develop the app with the user experience in mind.
3. Thoroughly Research the Market: Conduct thorough market research to understand your target audience, competition, and market trends. This information will help you make informed decisions and differentiate your app from others.
4. Plan Ahead: Develop a detailed project plan that includes timelines, milestones, and resources required. This helps organize the development process and ensures that you stay on track.
5. Use an Agile Development Methodology: Consider using an agile development methodology that uses iterative development and frequent testing. This approach allows for flexibility, adaptability, and quicker feedback loops.
6. Establish Regular Communication: Maintain regular and open communication with your development team. Clearly communicate your requirements, expectations, and any changes throughout the project. Collaboration and transparency are essential for success.
7. Test for Quality Assurance: Ensure thorough testing and quality assurance throughout development. Test your app on different devices, operating systems, and network conditions to ensure compatibility and performance.
8. Optimize App Performance: Pay attention to optimizing your app’s performance, including factors such as speed, responsiveness, and battery consumption. Users expect smooth and efficient app experiences.
9. Engage in App Store Optimization (ASO): Invest time and effort into optimizing your app’s visibility in app stores. Focus on factors like relevant keywords, compelling app descriptions, high-quality visuals, and positive user reviews.
10. Provide Post-launch Support and Updates: Launching the app is just the beginning. Provide regular updates, bug fixes, and feature enhancements based on user feedback and market trends. Continuously improve and refine your app to meet user expectations.
By following these tips, you can increase the chances of developing a successful mobile app that meets user needs, stands out in the market, and delivers a great user experience. Remember to adapt and learn from each project to improve future development endeavors.
LEARN MORE: Tips for Successful Mobile App Development Projects
Mobile App Security: Best Practices and Threats to Consider
Mobile app security is paramount to protect user data, prevent unauthorized access, and ensure the overall integrity of the app. Here are some mobile app security best practices to consider, along with common threats:
Secure Data Transmission
Ensure that sensitive data transmitted between the mobile app and servers is encrypted using secure protocols such as HTTPS or SSL/TLS. This prevents interception and eavesdropping by attackers.
Implement Strong Authentication
Utilize strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), to enhance the security of user accounts. Avoid relying solely on weak passwords and consider options like biometric authentication (fingerprint, facial recognition) for added security.
Use Code Obfuscation
Apply code obfuscation techniques to make it harder for attackers to reverse engineer or analyze the app’s source code. Obfuscation helps protect proprietary algorithms, critical business logic, and other sensitive information.
Regularly Update Libraries and Frameworks
Keep the mobile app’s libraries, frameworks, and dependencies current. Updates often include security patches that address vulnerabilities. Regularly check for updates and promptly apply them to reduce the risk of known security issues.
Securely Store Data
Implement proper data storage mechanisms, such as encrypting sensitive data at rest, to protect user information stored on the device. Leverage platform-specific secure storage options, such as Keychain on iOS or Keystore on Android, to store sensitive data securely.
Implement Secure Session Management
Ensure that sessions are securely managed within the app, including proper session timeouts, secure session token handling, and protection against session hijacking or replay attacks.
Implement Input Sanitization
Validate and sanitize all user input to prevent common security vulnerabilities such as injection attacks (SQL, OS, or XSS). To mitigate these risks, apply input validation and sanitization techniques on both the client and server sides.
Conduct Security Audits
Regularly perform comprehensive penetration testing and security audits on your mobile app. This helps identify vulnerabilities, weaknesses, and potential attack vectors. Engage security professionals to conduct thorough assessments and penetration testing to uncover vulnerabilities.
Monitor and Respond to Security Incidents
Implement mechanisms to monitor and detect security incidents in real time. Establish incident response protocols and processes to promptly address and mitigate security breaches, including notifying affected users and taking necessary actions to protect their data.
Common mobile app security threats include:
- Data breaches and unauthorized access
- Malware and malicious apps
- Man-in-the-middle attacks
- Code injection attacks
- Insecure data storage
- Insufficient authentication and authorization mechanisms
- Social engineering and phishing attacks
- Reverse engineering and intellectual property theft
By implementing these best practices and staying vigilant against potential threats, you can significantly enhance the security of your mobile app and protect user data and privacy.
LEARN MORE: Mobile App Security: Best Practices And Threats To Consider
The Importance of Mobile App Testing and Quality Assurance
Mobile app testing and quality assurance are crucial aspects of the app development process. They play a vital role in ensuring the success and effectiveness of mobile applications. Here are some key areas to focus on during the testing and quality assurance phase.
The User Experience
Mobile app testing helps ensure a smooth and seamless user experience. By thoroughly testing the app across different devices, operating systems, and network conditions, developers can identify and fix any issues that may negatively impact the user experience. This includes detecting and resolving bugs, crashes, slow performance, and usability issues.
Functionality and Reliability
Testing verifies that the app functions as intended and delivers the expected features and functionalities. It helps identify functional defects, such as incorrect calculations, broken links, or malfunctioning buttons. Quality assurance checks that the app operates reliably under various scenarios, such as handling high user loads, network interruptions, or resource constraints.
Compatibility
Mobile devices come in various screen sizes, resolutions, and hardware configurations. App testing helps ensure compatibility across different devices, operating systems, and versions. It helps identify and address issues related to device-specific functionalities, ensuring the app works seamlessly across a wide range of devices.
Security
Mobile apps often handle sensitive user data, such as personal information, financial details, or login credentials. Quality assurance includes security testing to identify vulnerabilities and weaknesses that malicious actors could exploit. This helps protect user data and ensures the app meets industry security standards and best practices.
Performance
Testing and quality assurance help evaluate and optimize the performance of the app. This includes assessing factors like response times, loading times, memory usage, battery consumption, and network efficiency. Developers can enhance the app’s speed, efficiency, and resource utilization by identifying and resolving performance bottlenecks.
App Store Compliance
App stores have strict guidelines and policies that developers must adhere to for their apps to be accepted and distributed. Mobile app testing helps ensure compliance with these guidelines, reducing the chances of rejection or removal from app stores. It includes validating app functionality, user interface design, content appropriateness, and adherence to platform-specific requirements.
Cost and Time Efficiency
Detecting and fixing issues early in the development lifecycle is more cost-effective and time-efficient than addressing them after the app is released. Testing and quality assurance help identify and resolve problems before the app reaches users, reducing support costs, negative reviews, and potential revenue loss.
Overall, mobile app testing and quality assurance are critical to delivering a high-quality, reliable, and user-friendly app that meets user expectations, performs well across devices, and ensures the security and privacy of user data. It helps build user trust, increases app adoption and engagement, and ultimately contributes to the success of your app in the competitive mobile app market.
LEARN MORE: The Importance Of Mobile App Testing And Quality Assurance
Understanding Mobile App Analytics and How to Use Them
Mobile app analytics are tools and techniques used to understand how people use mobile apps. They help you and your developers learn important information about your app, such as how many people use it, how long they use it, and what actions they take.
This data can be used in many helpful ways. For example, if droves of users abandon your app, the developers can pinpoint what’s wrong and fix it. They can also see which features are popular and which ones aren’t used much so that they can make improvements. App analytics can also help you determine how to make money from your app by revealing which ads or purchases generate the most revenue.
App analytics work by collecting data from the app users. This data can include things like how often the app is opened, which buttons are clicked, and which screens are visited. The data is then analyzed to find patterns and insights that can help improve the app.
In simple terms, mobile app analytics are like detectives that help you understand how people use your app and what you can do to improve it. They are powerful tools for creating apps that people love to use.
LEARN MORE: Understanding Mobile App Analytics And How To Use Them
The Importance of User Feedback in Mobile App Development
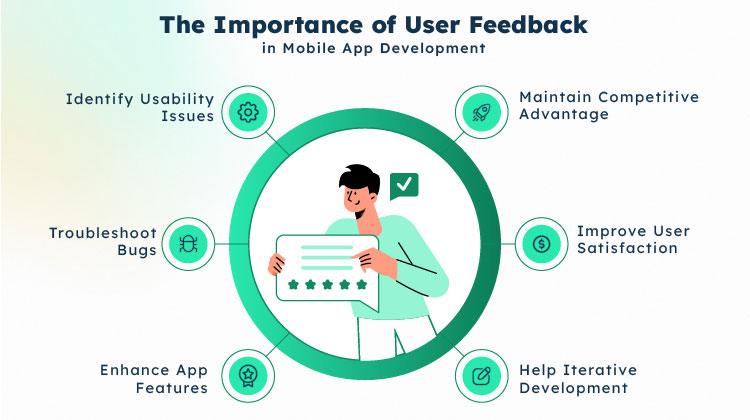
User feedback also plays a crucial role in improving your mobile app. When you track and analyze the comments and reviews you get from your users, you get valuable data to help you improve your app and deliver the functionality that will keep users coming back for more.
Identify Usability Issues
User feedback helps uncover usability issues and user experience problems that may not be apparent during development. Users can provide insights into navigation difficulties, confusing interfaces, or functionality that doesn’t meet their expectations. This feedback allows you to make necessary improvements and enhance the app’s usability.
Troubleshoot Bugs
Users often encounter bugs or technical glitches that developers may not have anticipated during testing. User feedback helps identify these issues, allowing developers to address them promptly. By addressing bugs and technical issues reported by users, developers can improve the stability and reliability of the app.
Enhance App Features
Users provide suggestions and ideas for new features or improvements to existing ones. This feedback helps developers understand user needs and preferences better. By incorporating user suggestions, developers can enhance app functionality, add valuable features, and tailor the app to better meet user expectations.
Improve User Satisfaction
Listening to user feedback and addressing their concerns demonstrates that developers value their opinions and are committed to improving the app. This improves user satisfaction and fosters a positive relationship between the users and the development team. Satisfied users are more likely to continue using the app, recommend it to others, and leave positive reviews, ultimately benefiting the app’s reputation and success.
Maintain Competitive Advantage
User feedback provides valuable insights into users’ experiences with competing apps. By analyzing user feedback, developers can better understand their app’s strengths and weaknesses compared to similar apps. This knowledge allows them to make strategic decisions, differentiate their app, and offer a better user experience, giving them a competitive edge.
Help Iterative Development
Mobile app development is iterative, and user feedback helps drive this iteration. Developers can release updates and new versions based on user feedback, continuously improving the app and addressing user concerns. User feedback acts as a valuable feedback loop, guiding developers throughout the development lifecycle.
By actively seeking and incorporating user feedback, you can create better, more user-centric apps that meet the needs and expectations of your target audience.
LEARN MORE: The Importance of User Feedback in Mobile App Development
How Much Does It Cost to Develop a Mobile App?
Trying to price mobile app development is like asking, “How much does a car cost?” The answer depends on the type of car you want. A luxury car with all the bells and whistles will cost you much more than a basic commuter car.
The same is true of mobile app development. Generally, you will pay $20,000 to $500,000, depending on the app’s complexity.
A basic mobile app with elementary logic and basic UI, built for a single platform (i.e., Android or iOS, but not both), will cost between $20,000 to $50,000 to develop.
The next step up would be an app with medium complexity—a couple of complex features, intermediate business logic, maybe some custom UI work or animations. Now you’re into the $50,000 to $100,000 range. Again, this would be a single-platform app.
If you need a complex app with many features, advanced logic, custom UI, a complicated architecture, and so on, the price tag will run anywhere from $100,000 to $500,000 or more—and that’s still for a single platform.
Building an app for both the iOS and Android platforms could drive up the cost of any app.
Reduce Costs by Outsourcing
You may be able to reduce costs by outsourcing mobile app development. A custom software development company may be able to tap into remote, offshore teams to reduce development costs while still delivering a high-quality app.
To get an accurate cost estimate from a mobile app development company, make sure you give them a complete picture of what you expect the app to do—the features you want, the platforms you need it to operate on, the databases and other software it will interface with, and so on.
How to Hire the Right Mobile App Development Company
If you decide to outsource the work, how do you choose the right mobile app development company for your needs? Here are six things to look at when evaluating a development partner.
1. Client Reviews
The quickest way to get a feel of a potential development partner is to see what others say about them. Review sites abound, making it barely an inconvenience to discover what it’s like to work with them. Check Google Reviews, Clutch.co, GoodFirms.co, DesignRush and the company’s website to find out what it’s like to work with them.
You can also ask for references. Not only will you get answers to specific questions from their existing clients, but it also shows that your potential development partner isn’t worried about what you’ll learn.
2. Company Culture
You’ll work with the team you choose for several weeks, so make sure it’s a team you’ll like working with. They should listen more than talk. They should be able to empathize with your business needs and your user’s needs. And they should be dedicated to craftsmanship and future-focused.
Your development team should also genuinely enjoy their work. Great mobile app development takes more than hiring skilled people. If everyone feels heard and supported, they can do their best and most innovative work.
A company with these core elements woven into its culture will more likely deliver a quality product.
3. Experience
Check to see if the company has experience building mobile apps like yours. If so, they can apply the lessons they learned on previous projects to accelerate your project’s development cycle and increase the final product’s quality.
If their experience doesn’t precisely align with your needs, it’s not necessarily a strike against them. As long as they keep up with mobile app development trends, they should still be able to deliver a high-quality product. But if you’re having trouble choosing between two similar companies, the one that’s done similar work before might be your best bet.
4. Velocity
Delivering software on time is always important, but for mobile apps, it can mean the difference between success and failure. If you’re trying to beat a competitor to market or capitalize on a trend you see developing, missing your launch date makes it harder to achieve the success you expected.
The key to meeting release dates and deadlines is their software development methodology. Ask them to walk you through their development process. Are they Agile? How do they track and report project status? What’s the level of transparency?
A high level of transparency helps keep the project on schedule. By alerting you of delays early enough, you have time to change tactics and mitigate the impact of the delay.
5. Cost
As you evaluate potential development partners, get detailed cost estimates. You need to know the total development cost and a breakdown of that cost. This allows you to compare apples to apples.
Ask potential mobile app partners to show how they estimate each feature. If every development company’s total cost exceeds your budget, you might be able to choose low-priority features to drop from the project to bring the cost down.
While it’s tempting to partner with a “rock star” software development company, those firms often charge a premium for their services because they’re in high demand. In other words, you pay more for the same services and quality you could get from a lesser-known company.
6. Support and Maintenance
Finally, ask your prospective mobile app partners what happens after release. What level of support and maintenance is included in the estimate?
Apps often have bugs that aren’t found until they get into the hands of users. Operating system updates can impact app functionality, too. When your customers report a bug, you need to get it fixed quickly to keep it from hurting your brand and the app’s success.
The level of maintenance and support you get depends on the mobile app developer. Make sure the developer you partner with offers technical maintenance and support for bug fixes and upgrades.
LEARN MORE: How to Hire the Right Mobile App Development Company
How to Monetize Your Mobile App
How much you spend building a mobile app depends on how much you expect to make from it once it’s built.
If you’re developing the app for internal business uses, you need to know up front how it will benefit your bottom line. Will it reduce costs? Get your products to market faster? Help you retain customers?
If you’re developing a commercial app, will you charge for it upfront? Make it subscription-based? Or will you offer it for free and make money by selling ads or offering in-app purchases?
The various benefits and optimization methods for monetizing your mobile app could fill an entire book. It’s another area where an experienced mobile app developer can guide you.
Knowing how you’ll monetize the app will influence the design. If you’re going to sell ads, developers will need to know how much screen real estate to devote to an ad and what type of ad it is. Banner ads are coded differently than interstitial ads, video ads, and so on. They also impact app performance in different ways.
You may want to use multiple methods—for example, combining a subscription-based model with in-app purchases. Keep in mind how your monetization model will affect the user experience; if you frustrate users with constant ads or interruptions, your app may receive a low rating, and customers will stop using it.
Figuring out how to make money from your mobile app is complicated, but it’s critical to the app’s success.
LEARN MORE: Maximizing Profits: How To Monetize Your Mobile App
Understanding the Different Mobile App Store Guidelines
Mobile app store guidelines provide a set of rules and requirements for developers to follow when submitting their apps for distribution on the various app stores. The four leading app stores are the Apple App Store, the Google Play Store, the Microsoft Store, and the Amazon Appstore. Here’s a quick overview of the stores and their guidelines.
Apple App Store
- Apps must be functional, reliable, and provide a high-quality user experience.
- They must comply with Apple’s design and user interface guidelines.
- Apps should not contain offensive, malicious, or misleading content.
- Privacy and data security are crucial, and apps must request user consent for data collection and adhere to Apple’s App Tracking Transparency framework.
- In-app purchases and subscriptions should follow Apple’s guidelines.
- Apps that provide digital goods or services must use Apple’s in-app purchase system and share a portion of revenue with Apple.
Google Play Store
- Apps should be stable, safe, and offer a good user experience.
- They should follow Google’s design guidelines and policies.
- Apps must not contain inappropriate, offensive, or harmful content.
- Developers must respect user privacy and handle personal data responsibly.
- In-app purchases must use Google Play’s billing system, and the appropriate revenue share with Google is required.
- Apps should not violate intellectual property rights or engage in deceptive practices.
Microsoft Store
- Apps must provide a positive user experience and adhere to Microsoft’s design principles.
- They should not contain offensive, illegal, or harmful content.
- Developers must respect user privacy and handle personal data securely.
- In-app purchases and subscriptions should follow Microsoft’s guidelines.
- Apps should not infringe on intellectual property rights and must comply with regional laws and regulations.
Amazon Appstore
- Apps should be functional, reliable, and provide a good user experience.
- They must comply with Amazon’s content guidelines and policies.
- Apps should not contain offensive, illegal, or misleading content.
- Developers must respect user privacy and handle personal data responsibly.
- In-app purchases should use Amazon’s in-app purchasing system.
It’s essential to thoroughly review the specific guidelines for each app store you plan to distribute your app on, as the guidelines may change over time.
LEARN MORE: Understanding The Different Mobile App Store Guidelines
Common Mobile App Development Mistakes to Avoid
To ensure your mobile app stands out from the competition, avoid the typical app development mistakes many business owners make.
Don’t Develop a Mobile App No One Needs
Take a good, hard look at your app idea and ask yourself, “Is this a problem worth solving?” Get an outside, unbiased perspective. Determine your business’s challenges and the requirements of your users. Then see if a mobile app can solve those challenges in a way that satisfies the end users. If it does, continue developing the app.
Don’t Skimp on Your Research
In the same vein, thoroughly research the market, the industry, and your potential customers’ needs before deciding to develop a mobile app. Every business has a different set of goals. Thorough research can save you a lot of funding.
Don’t Set an Unrealistic Budget
Developing a mobile app is a significant financial commitment. Remember, you get what you pay for. Taking the cheaper path may not deliver the best results. Discuss requirements and objectives with your development team before setting the budget.
Don’t Be Vague
One way to budget appropriately is to clearly communicate your product vision at the outset. If the developers know exactly what needs to be accomplished and how much time it will take, they can estimate costs more realistically. Explain precisely what features you need the app to have. Create flowcharts, diagrams, and sample sketches of the screens to help your designers and developers see what you see in your mind’s eye.
Don’t Include Too Many Features
Start simple. Make sure the app serves the primary purpose of your business. You can slowly introduce new features when you have more customer feedback to guide you. That way, you’re not paying for features no one uses.
Don’t Build a Single-Platform App
Use a cross-platform strategy for your app. While there are some downsides to developing a cross-platform mobile app, it’s usually the best way to maximize your customer reach. A cross-platform app lets you test the market and decide whether to use the hybrid approach or switch to a native app.
Don’t Get Hung Up on Looks
The user experience will make or break your app. Don’t focus too much on making a cool-looking app and forget your customers’ needs. Make sure the UX/UI design is clean, intuitive, and serves the end-user objective. Your users should be able to navigate through various screens quickly to do what they need to do.
Don’t Neglect Your Marketing Strategy
Before investing in app development, take time to plan a marketing strategy. It may seem like putting the cart before the horse, but app stores are very competitive arenas. Thousands of new apps are released every day. It’s nearly impossible for your app to sell itself without a good marketing plan.
LEARN MORE: Common Mobile App Development Mistakes to Avoid: A Comprehensive Guide
How to Improve Your Mobile App’s Performance
Your customers expect high app performance. If your app takes too long to launch or lags whenever they enter information, users may get frustrated. And if it drives up their data charges or runs their battery down by constantly pulling data, they’ll likely ditch your app.
To improve your app’s performance, take the following steps:
- Analyze user feedback for common complaints.
- Study your app’s behavior for the root cause(s).
- Determine one change that will make the most significant improvement.
- Make the change.
- See if the app performance improves.
Even if you’re not getting user complaints or seeing performance issues, run through the cycle above regularly to keep your app performing well.
LEARN MORE: How To Improve Your Mobile App’s Performance
The Future of Mobile App Development: Trends and Predictions
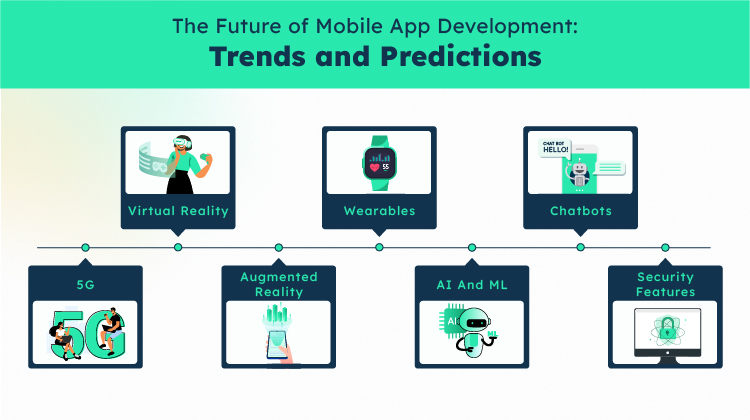
Mobile app development is constantly evolving. Technologies like 5G, augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR), and wearable devices have significantly impacted how apps are developed and used. Let’s look at a few trends that are predicted to impact mobile app development in the next year.
5G
5G networks offer faster download and upload speeds and lower latency. These speeds allow developers to create more complex and sophisticated apps that require real-time data processing.
By improving data streaming potential, reducing latency, and boosting reliability, 5G has given mobile app development much more flexibility to create faster, feature-rich, and more attractive apps.
Virtual Reality
The speed 5G networks coupled with more powerful mobile device processors will also enable the development of more immersive and interactive apps, such as AR and VR experiences.
The primary use case for VR is gaming and entertainment, but a few organizations are exploring VR for education and training.
Augmented Reality
Once an abandoned technology, major tech companies are working on augmented reality (AR) devices again. And the technology shows promise for mobile app developers. Mobile apps can leverage AR for shopping, transportation, logistics, medicine, education, entertainment, gaming, and a near-endless list of other applications.
Google and Apple are expected to announce AR devices later this year.
Wearables
As wearables get more powerful, mobile app developers are building independent apps specifically for these devices. Native apps for wearables will likely be a mobile app development trend that lasts for the next few years.
AI and ML
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) exploded in popularity at the end of 2022, and the trend shows no signs of slowing down. AI has pros and cons, but it’s hard to deny that the mobile app industry is quickly adopting the technology.
Additionally, you can use AI to analyze large amounts of data to make predictions and recommendations based on user activity. It can even provide insights to help developers improve the overall performance of an app.
Chatbots
Chatbots have been around for a long time, so it may seem odd to call them a mobile application development “trend.” However, the advances discussed above—namely 5G and AI—will make building responsive, human-like chatbots into your mobile apps easier.
Security Features
As the importance of data security and privacy increases, mobile apps will need to focus on robust security measures. That means implementing stronger encryption techniques, biometric authentication, and compliance with privacy regulations to protect user data.
Embracing these trends will enable you to create innovative, user-centric, and immersive mobile apps that cater to evolving user expectations and industry demands.
LEARN MORE: The Future Of Mobile App Development: Trends And Predictions
Mobile App Development for Enterprise: Challenges and Opportunities
Mobile app development for the enterprise presents both challenges and opportunities. Here are some of the critical challenges and opportunities faced in this domain.
Challenges
1. Security: Enterprise mobile apps often handle sensitive business data, making security a top concern. Protecting data during transmission, storage, and securely handling user authentication are critical challenges.
2. Integration with Existing Systems: Many enterprises have complex IT infrastructures with legacy systems. Integrating mobile apps with these systems, such as CRM, ERP, or databases, can be challenging due to compatibility issues and the need for seamless data synchronization.
3. Scalability: Enterprise apps need to handle a large number of users and scale seamlessly as the user base grows. Ensuring optimal performance, load balancing, and maintaining responsiveness under high user loads are significant challenges.
4. Compliance and Regulation: Enterprises must comply with industry-specific regulations and data privacy laws. Mobile apps must adhere to these regulations, such as GDPR or HIPAA, which require robust security measures and data handling practices.
5. User Adoption and Engagement: Encouraging employees or users to adopt and actively use enterprise mobile apps can be challenging. Designing intuitive user interfaces, providing clear value propositions, and offering training and support are critical for user adoption and engagement.
Opportunities
1. Increased Productivity: Enterprise mobile apps offer the opportunity to streamline and automate business processes, resulting in increased productivity. Apps can provide functionalities like mobile access to corporate data, task management, collaboration tools, and real-time communication, enabling employees to work efficiently from anywhere.
2. Enhanced Customer Experience: Mobile apps allow enterprises to engage with customers in a personalized and convenient manner. Apps can provide self-service features, personalized offers, real-time support, and seamless transactions, improving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
3. Data Analytics and Insights: Mobile apps capture valuable user data, giving enterprises insights into user behavior, preferences, and trends. By leveraging data analytics, enterprises can make data-driven decisions, optimize business strategies, and offer personalized experiences.
4. Empowering a Mobile Workforce: Mobile apps empower a mobile workforce, enabling employees to access relevant information, collaborate, and perform tasks on the go. This flexibility improves efficiency, communication, and teamwork, benefiting the enterprise as a whole.
5. Competitive Advantage: A well-designed and innovative enterprise mobile app can provide a competitive edge in the market. It can differentiate the enterprise from competitors, attract new customers, improve brand perception, and drive business growth.
6. Cost Savings: Mobile apps can reduce operational costs by automating manual processes and enabling self-service. For example, apps that offer customer support or allow remote working can reduce the need for physical infrastructure, leading to cost savings.
7. Innovation and Digital Transformation: Enterprise mobile apps can be a catalyst for innovation and digital transformation within an organization. They enable enterprises to embrace new technologies, optimize workflows, and adapt to changing market demands.
By addressing these challenges and leveraging the opportunities, enterprises can successfully develop and deploy mobile apps that streamline operations, improve productivity, and drive business growth.
LEARN MORE: Mobile App Development For Enterprise: Challenges And Opportunities
Are You Ready for Mobile App Development?
Hopefully, this guide has given you a solid overview of what’s involved in building a mobile app for your business. So what’s next?
You’ll need to decide what type of app you want to build, how it will improve your revenue, what technologies and platforms are best for your needs, and whether or not you can build the app with your in-house talent.
If you decide to outsource the development of your mobile app, you’ll need to research custom software development companies that specialize in mobile apps—notably, the kind of app you want to build.